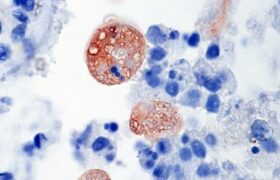
Amibiase
Amoebiasis is the third deadliest parasitic disease in the world. The large majority of infected persons often present no symptoms, but in some cases infection lead to clinical complications....
The research teams of the Labex IBEID work on understanding, preventing, and treating numerous infectious diseases.
Find here a reliable and clear source of information to understand the world around us. Consult the disease fact sheets detailed in alphabetical order.

Amoebiasis is the third deadliest parasitic disease in the world. The large majority of infected persons often present no symptoms, but in some cases infection lead to clinical complications....
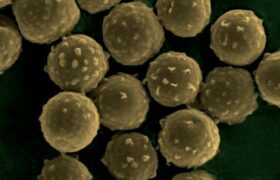
Aspergillosis is a term that refers to any infection caused by fungus (mold) belonging to the genus Aspergillus, whose spores are present in the air and breathed in by people every day. While Aspergil...
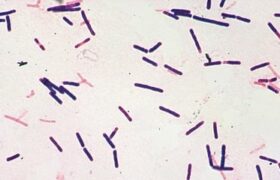
Botulism is a severe neurological disease caused by a highly potent toxin produced by Clostridium botulinum bacteria. There are different types of botulism: foodborne botulism, infant botulism and wou...
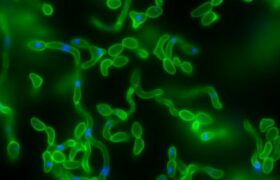
Fungi (yeast) of the Candida genus can cause superficial infections affecting the mucous membranes or skin, and invasive infections, either localized to one organ or generalized throughout the body. C...
The chikungunya virus is transmitted by specific mosquito species. This infection causes severe, and sometimes persistent, joint pain in affected patients. Mainly endemic in South Asia and Africa, thi...

Chlamydia is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis. It is the most widespread bacterial STI, affecting both men and women, and is particularly common amo...
Cholera is an infectious, diarrheal, strictly human disease caused by specific bacteria of the species Vibrio cholerae. The World Health Organization estimates that there are nearly 3 million cases of...
Whooping cough, long thought of as a childhood illness, can actually be severe at any age. It is particularly dangerous, and sometimes even fatal, for unvaccinated or partially vaccinated infants and ...
Coivd-19 is a highly contagious emerging infectious disease spreading by airborne transmission and surface contamination. Although COVID-19 can be asymptomatic, it can also cause a variety of symptoms...
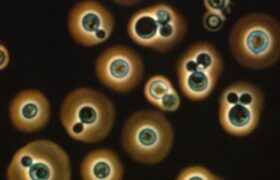
Cryptococcosis is a severe fungal infection mainly caused by the fungus Cryptococcus neoformans. this infection occurs in immunocompromised patients and the most frequent clinical form of infection is...
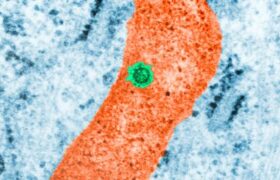
Dengue, also known as ‘tropical flu’, is an infectious disease caused by the virus of the same name. The virus is transmitted by specific mosquitoes. The incidence of dengue is rising rapidly and ...

Diphtheria is a disease caused by several Corynebacterium species. Diphtheria typically manifests as a respiratory infection that causes impairment of the central nervous system, the throat and other ...
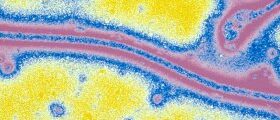
The Ebola virus causes high fever and bleeding that can often prove fatal. The death rate varies between 30 and 90% depending on the outbreak and virus species. Bats are believed to be the natural res...

Escherichia coli (E. coli) is a bacterium that lives in the digestive tract of humans and warm-blooded animals. Most strains of E. coli are harmless, but a small number can lead to illness for humans....
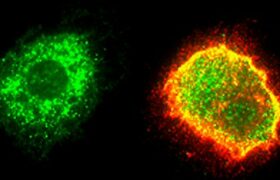
Lassa fever is a hemorrhagic disease caused by the Lassa virus. It is endemic in several countries in West Africa, where it infects 100,000 to 300,000 people every year, claiming 5,000 to 6,000 lives....

Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever (CCHF) is a disease caused by a virus of the same name. The main route of transmission of the virus to humans is bites from ticks. In most cases, the infection is mild,...
Yellow fever is a viral disease caused by the virus. If the disease typically begins with fever, chills, muscular pain and headaches, it could evolve in serious forms with the onset of a hemorrhagic s...

Typhoid and paratyphoid fever are infectious diseases caused by Salmonella bacteria, that can be fatal if left untreated. They generally occur in regions with low standards of hygiene and cause consta...
nfluenza is a contagious respiratory infection caused by influenza viruses, which are unique due to their vast genetic variability. It is a public health issue because of the seasonal outbreaks that a...
Avian influenza is a viral disease that affects birds, with a very high mortality rate in farmed birds such as chickens and geese. Although most avian viruses do not infect humans, some subtypes are a...
Viral hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver caused by viruses. To date, five viruses have been identified that target the liver and cause inflammatory infection. These viruses are referred to by t...
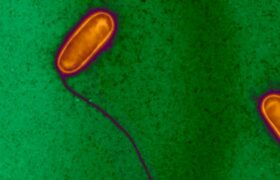
Legionellosis is a collective term for diseases caused by Legionella bacteria, including the potentially fatal Legionnaires' disease. The most common species, Legionella pneumophila, causes a severe l...
Leishmaniases are parasitic diseases causing severely debilitating cutaneous or visceral lesions, which can prove fatal if left untreated. They are caused by various parasites of the genus Leishmania,...
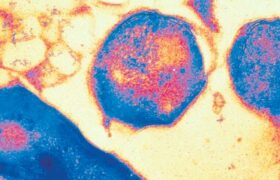
Leprosy is a chronic bacterial condition caused by the Mycobacterium leprae bacterium infections. The disease causes skin lesions and nerve damage. Without treatment, these lesions develop and become ...

Leptospirosis is a bacterial disease found throughout the world caused by the some Leptospira bacteria species. Its main reservoirs are rodents, particularly rats, which excrete the bacterium in their...
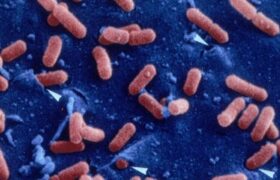
Listeriosis is a severe foodborne infection caused by the bacterium Listeria monocytogenes. It can cause septicemia and central nervous system infections. In pregnant women, it can cause miscarriage, ...
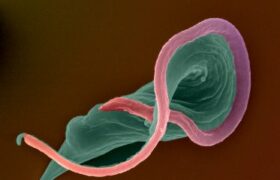
Chagas disease is a neglected parasitic infection. It is transmitted by a hematophagous insect, known as triatomine bugs. In some cases, the infection takes a chronic form, causing irreversible lesion...

Lyme disease, also known as Lyme borreliosis, is a tick-transmitted zoonosis. It is the most widespread vector-borne disease in the whole of the northern hemisphere. Its incidence continues to rise at...
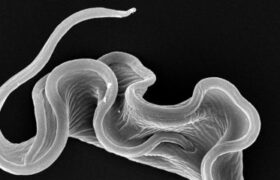
Sleeping sickness, also known as African trypanosomiasis, is caused by the parasitic flagellate Trypanosoma brucei, which is injected into the body by the tsetse fly. The disease occurs only in the 36...
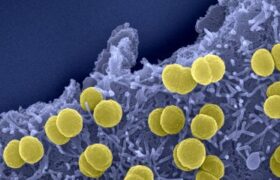
Meningitis is an infection of the brain membranes – or meninges – caused by several types of virus, bacteria and fungi. Meningococcus (another name for the Neisseria meningitidis bacterium) is one...
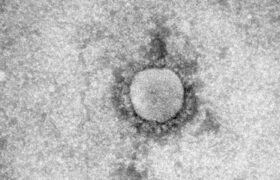
MERS-CoV, or Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus, is a virus affecting the respiratory tract, causing fever and a cough and proving fatal in 30% of cases. ...
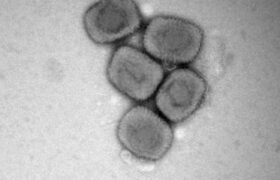
Monkeypox is a disease caused by the monkeypox virus (MPXV) that was initially present in animals, and now circulates among humans – it is referred to as an emerging zoonotic disease. It presents as...
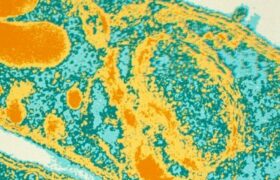
Malaria is a disease caused by parasites of the Plasmodium genus transmitted to humans via bites from infected mosquitoes. The clinical presentation of malaria is not specific. The disease starts with...
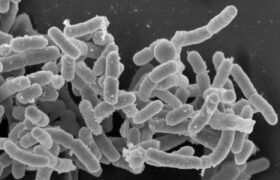
Plague is still rife in Africa, Asia and America, is counted among the world's re-emerging diseases, and is subject to international regulations. Plague is a rodent disease, mainly carried by rats, an...

Poliomyelitis is a highly contagious disease caused by a virus, the poliovirus, which invades the nervous system and can lead to irreversible paralysis in just a few hours. ...
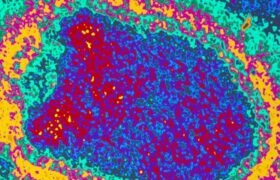
Rabies is caused by the transmission of certain lyssaviruses through bites by an animal. Dogs and bats are the main vectors of transmission to humans. The rabies virus is neurotropic: it infects the n...

Salmonella is a genus of the Enterobacteriaceae family that is responsible for cases of foodborne illness, also known as salmonellosis. Most Salmonella bacteria are hosted in the intestines of vertebr...
Sepsis is the term used internationally to describe a widespread inflammatory response that occurs as a result of severe infection. Septicemia refers to the presence of bacteria (or fungi or viruses) ...
Shigellosis is a highly contagious diarrheal disease, caused by Shigella bacteria which are specialized clones of Escherichia coli. This disease is responsible of outbreaks occurring throughout the w...
SARS (severe acute respiratory syndrome) is caused by a coronavirus known as SARS-CoV-1. It was the first severe transmissible disease to emerge in the 21st century. ...
Staphylococci are pathogenic bacteria causing a broad spectrum of diseases with varying degrees of severity. They are one of the main agents of nosocomial infections (hospital-acquired infections) but...
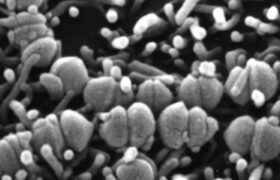
Infections with group A and B Streptococcus are frequent. The two bacteria are part of the commensal flora and they only cause symptoms in certain conditions (opportunistic pathogens) or in people at ...
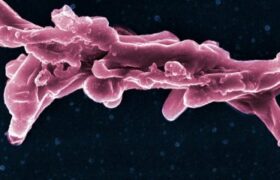
TB is a contagious disease caused by Koch's bacillus (strains of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex). This infectious agent is spread through the air via bacteria-laden droplets produced when TB p...
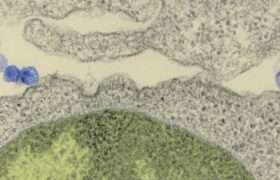
HIV targets and destroys T cells, white blood cells that play an essential role in the immune system. Over the long term, infected individuals can therefore develop what are known as "opportunistic" d...
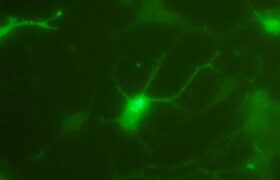
West Nile virus is transmitted to humans by mosquitoes. It causes sudden fever, sometimes associated with neurological complications that can be severe in many animal species. It is currently endemic ...
The Zika virus is transmitted by specific mosquitoes. The disease caused by the virus have symptoms which resemble those of the dengue virus or chikungunya including fever, headaches, skin rash, tired...